SVN到Git迁移笔记
本篇博文目的是将本地SVN服务器的project迁移为GIT格式,并上传到目前大家常用的github托管服务器.
解决方案:
一.环境部署
操作系统: centos6.3 x64
SVN: subversion-1.8.0
apache: httpd-2.4.4
svn server(centos6.3 x64): node2.example.com
svn client(centos6.3 x64): node1.example.com
git server: https://github.com/leonIi/
一.关闭iptables和SELINUX
# service iptables stop
注:如需开启防火墙,则添加如下一条规则打开svn 3690端口
# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 3690 -j ACCEPT
# setenforce 0
# vi /etc/sysconfig/selinux
---------------
SELINUX=disabled
---------------
二.同步时间
# ntpdate cn.pool.ntp.org
三.安装apache
传送门:http://www.showerlee.com/archives/6
四.关闭系统自带svnserve
# service svnserve stop
# chkconfig svnserve off
注:本文档为了与apache2.4.4配合不发生兼容问题,所以使用了最新编译版本的svn,这里关闭是为了保证与rpm的版本不冲突.
五.安装svn server
传送门:http://www.showerlee.com/archives/350
注:安装完毕后:
svn根目录: /data/svn_repo
http访问URL: http://node2.example.com/svn/'具体仓库'
六.SVN到GIT迁移
1.首先在github上面创建一个repository(略)
2.创建一个SVN仓库(svn server)
# cd /data/svn_repo/
# svnadmin create project01
重启svn与apache
# killall svnserve
# /usr/local/svn/bin/svnserve -d -r /data/svn_repo/
# /usr/local/apache2/bin/apachectl restart
3.SVN checkin and checkout(svn client)
1).客户端安装svn(若安装可略过)
# yum install svn -y
2). svn checkout
# cd ~
# mkdir svn_client_repo
# cd svn_client_repo
# svn co http://node2.example.com/svn/project01
3). svn status
# svn status project01
# cd project01
# touch test01 test02 test03
4). svn add (添加)
# svn add test01
# svn add test02
# svn add test03
5). svn checkin(提交)
# svn ci -m”project01”
6). svn log (查看文件日志注释)
# svn log 1
常见错误提示:
Commit failed (details follow):
Error normalizing log message to internal format
Can't convert string from native encoding to 'UTF-8':
解决方法:
# vi ~/.subversion/config
修改:log-encoding = UTF-8
svn: Can't open file '/data/svn_repo/project01/db/txn-current-lock': Permission denied
解决方法:
将server端 /data/svn_repo/project01目录属主修改为apache用户,默认为daemon
# chown -R daemon.daemon /data/svn_repo/project01
2.使用git迁移(svn client)
1).客户端安装git(若安装可略过)
# yum install git* git-svn -y
# cd ~
# mkdir git_client_repo
# cd git_client_repo
建立SVN用户到git用户的映射文件
# echo "(no author) = test <test@123.com>" > userinfo.txt
# git svn init http://node2.example.com/svn/project01 project01
# cd project01
将svn用户映射到git上.
# git svn fetch --authors-file=../userinfo.txt
# git log
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
commit edc2cdd658f8844ad4a883d083b84ef5dad2320c
Author: test <test@123.com>
Date: Mon Aug 11 05:50:09 2014 +0000
project01
git-svn-id: http://node2.example.com/svn/project01@2 595a6c50-5861-48b1-ab0a-b1b54e0fc7cc
commit 9bde3c02fbfa6f22088b442a519cfd3870433ebc
Author: test <test@123.com>
Date: Fri Aug 8 07:55:54 2014 +0000
<E2><80><9D>project01<E2><80><9D>
git-svn-id: http://node2.example.com/svn/project01@1 595a6c50-5861-48b1-ab0a-b1b54e0fc7cc
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
当然上面的两步,可以作一步处理
# git svn clone http://node2.example.com/svn/project01 --authors-file=userinfo.txt project01
注: git svn fetch 这个步骤,可能碰到只想从某个版本开始进行fetch,那么请需要 –r 参数。
例如:
# git svn fetch -r 1342:HEAD
注:1342是你想要从这个版本开始fetch,如何查看这个版本号,你可以使用 svn 命令(windows下需要安装Subversion Client,e.g. sliksvn),简单使用就是 svn log svn_url
这个时候,你可能看到整屏在刷新,没关系,看到log就行。当然更简单的就是使用TortoiseSVN-> Show log。
亦或者你可以这样使用:
# git svn clone http://node2.example.com/svn/project01 -sr 1342:HEAD project01
2)创建本地SSH keys并上传到github,详见:
https://help.github.com/articles/generating-ssh-keys
并更改连接到github SSH端口
# vim ~/.ssh/config
增加:
————————————————————————————
Host github.com
Hostname ssh.github.com
Port 443
————————————————————————————
3).到这步的时候,本地已经clone了SVN仓库,现在需要的就是提交到远程了。首先,关联github远程仓库,如下:
# git remote add origin git@github.com:leonIi/project01
# git fetch
# git commit -a -m "add file"
# git add .
# git push -f
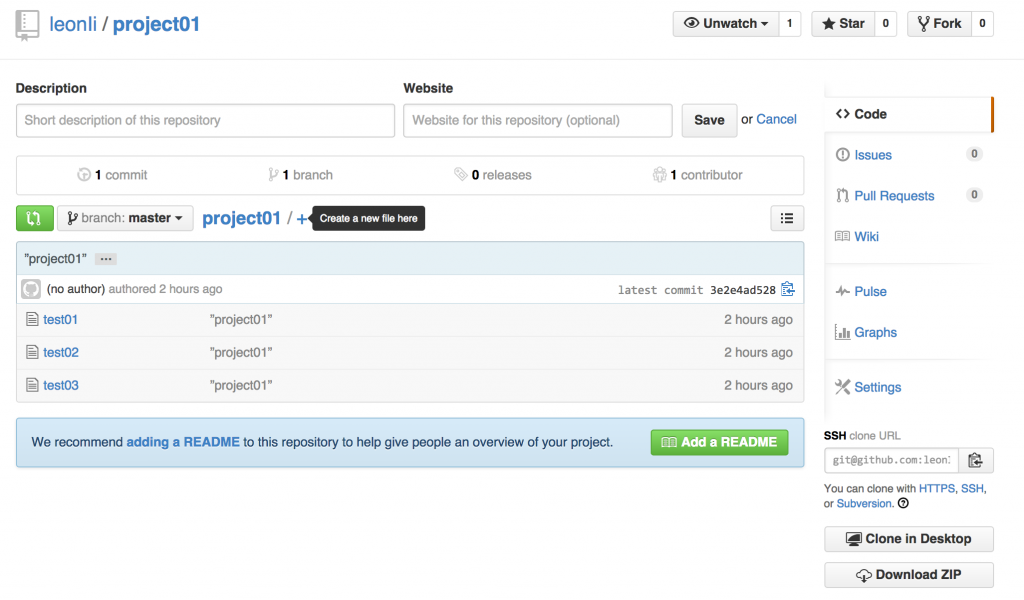
到github上面查看这个仓库(repository),大致效果如下(https://github.com/leonIi/project01.git)
大功告成…
本文链接:http://www.showerlee.com/archives/1227


还没有评论,快来抢沙发!